The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the numberRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the oddsPortantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcome

Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08
Odds ratio versus relative risk examples
Odds ratio versus relative risk examples- The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokersWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
The odds ratio and relative risk give us similar information, but we interpret each value in slightly different ways In particular The odds ratio tells us that the odds of passing the skills test is higher under the new program The relative risk tells us that the probability of passing the skills test is higher under the new programThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ; Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed) The risk
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group However, this wouldIn the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r
You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audience Die Odds Ratio beträgt dann 1,2%3,9% = 30,7% Anhand der Odds Ratio gemessen, ist die Wahrscheinlichkeit, sich den Magen zu verderben, in Uni Y um 30,7% höher als in Uni X Relatives Risiko (RR) Das Relative Risiko vergleicht auch zwei Gruppen In jeder Gruppe bezieht sich der „Fall" immer auf die Gesamtzahl, also jeweils auf alle 80348 f7450 doi 10 1136 / BMJ F7450 in the context of




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Understanding Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Related Terms As Simple As It Can Get Psychiatrist Com
The simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variableOdds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be used to approximate the relative risk of the event of Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases of




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology
Das relative Risiko ist, wie das Odds Ratio (OR), ein Maß für den Zusammenhang zwischen Therapien und einem Zielergebnis Das relative Risiko RR der Therapie A zu Therapie B ist definiert als Quotient der Wahrscheinlichkeiten P für das Eintreffen desThe odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretation that most people make There are someOdds Ratio, Relative Risk,Absolute Risk Reduction, and the Number Needed to Treat—Which of These Should We Use?



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Relative Risk Wikipedia
Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to noneventsThe risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisons by dividing the risk for one group (usually the group exposed to the risk factor) by the risk for the second, nonexposed, group This gives us the risk ratio Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Published on by Howard Herrell, MD Many great things have been written about the difference between Odds Ratios (OR) and Relative Risks (RR) Every medical student at some point has been taught the difference Yet these statistical terms are confused and misused every day in both the writing of and the




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08
Abstract The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks is feasible if meaningfulDes Odds Ratios als relatives Risiko zu einer Überschätzung des Therapieeffektes führen würde Das „Risiko" für einen Therapieerfolg ist in der DiclofenacGruppe im Vergleich zu Placebo ca 2mal so hoch (RR=2,08) und nicht 2,5mal so hoch (OR=2,47) Für beide Maßzahlen sind im Konfidenzintervall aus schließlich Werte enthalten, die für eine Überlegenheit von 50 mgA prevalence ratio, or ;



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other groupBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratioOdds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert Genau so kommen Experten auf populäre Zeilen wie "Gewöhnliche alkoholische Getränketrinker sind 24 mal mehr gefährdet, an Leberproblemen



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds ratio (OR), risk ratio (RR), and prevalence ratio (PR) are some of the measures of association which are often reported in research studies quantifying the relationship between an independent variable and the outcome of interest There has been much debate on the issue of which measure is appropriate to report depending on the study design However, the literature RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ; Since the relative risk is a simple ratio, errors tend to occur when the terms "more" or "less" are used Because it is a ratio and expresses how many times more probable the outcome is in the exposed group, the simplest solution is to incorporate the words "times the risk" or "times as high as" in your interpretation If you are interpreting a risk ratio, you will always be correct by




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
Commonly used point estimate proportion, relative risk, odds ratio TimetoEvent (Survival) Variables Examples time to progression, time to death, time to relapse Commonly used point estimates median survival, kyear survival, hazard ratio Other types of variables nominal categorical, ordinal categorical Today Point Estimates commonly seen (and misunderstood) in clinical oncology odds RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop a risk = odds/(1odds) "Most published research providing an odds ratio as a measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for the baseline risk, and hence the relative risk, to be calculated If numbers in each group are given, the crude relative risk can be calculated directly" – BMJ 14;348f7450 doi /bmjf7450




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge



2
The absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparableOdds ratio and relative riskEven an odds ratio;



2




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
Yes and no The risk ratio is collapsible, so adjusting for any variable that is not associated with either the exposure or outcome should not change the magnitude of the risk ratio In addition, the summary risk ratio across strata should be between the values of the stratumspecific risk ratios (something that does not hold with the odds ratio)Risk do not have to refer to undesirable outcome risk = odds / most published research providing odds ratio as measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for baseline risk, and hence relative risk, to be calculate If numbers in each group are give, crude relative risk can be calculated directly Bmj 14;The relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomes If IE is substantially smaller than IN , then IE/(IE IN) ≈ {\displaystyle \scriptstyle \approx } IE/IN



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh
If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occurEdna Schechtman, PhD Department of Industrial Engineering and Management, Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Beer Sheva, Israel ABSTRACT Introduction In recent years, the amount of available information in medical literature has increased rapidly, and It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
A rate ratio, ;Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert Genau so kommen Experten auf populäre Zeilen wie "Gewöhnliche alkoholische Getränketrinker sind 24 mal mehr gefährdet, an LeberproblemenA nonmemorization method of dealing with RR and OR*USMLE is a registered trademark of its respective holder I am in no way affiliated with itDisclaimer




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



2
The literature dealing with the relation between relative risk and odds ratio is quite extensive (some examples are (Da vies et al, 1998; The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an exampleSince it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used to approximate the relative risk of the event of interest The odds ratio should be used as an approximation to the relative risk




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
Das relative Risiko wird von anderen Risikoangaben unterschieden, zB vom absoluten Risiko, vom attributalen Risiko und von der Odds Ratio 3 Hintergrund Relative Risikoangaben können dazu benutzt werden, die Wahrnehmung eines Risikos zu verändern Dies wird häufig in Studien verwendet, um positive Ergebnisse gegenüber negativen



Case Control Study Wikiwand




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



1




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



1




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



2




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio On The Backpack And Back Pain Study Massage Fitness Magazine




First Aid Epidemiology Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
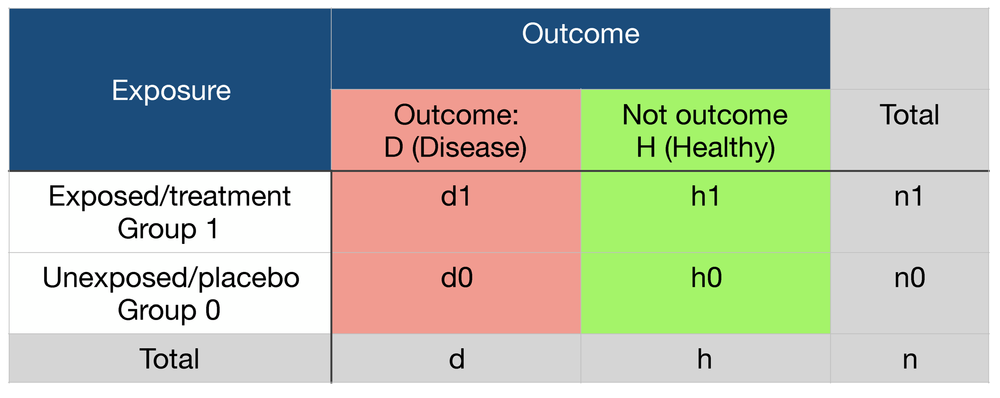



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
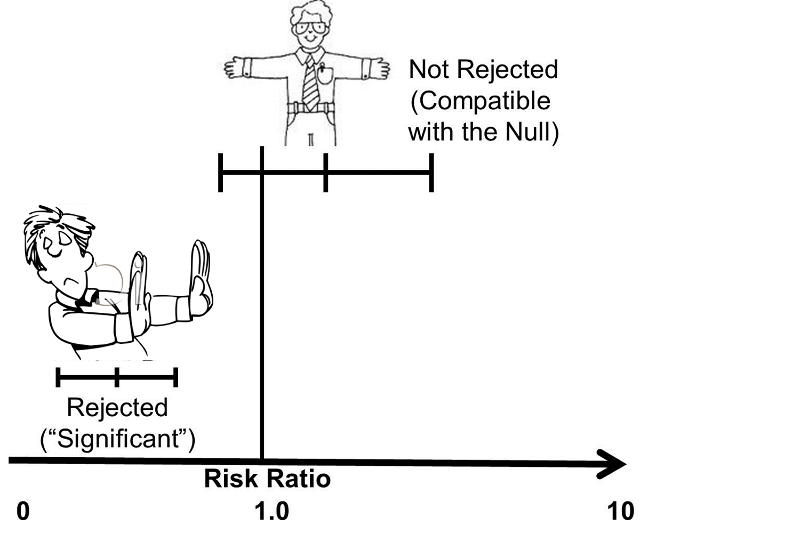



Confidence Intervals And P Values




Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Statistics Math Research Methods




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
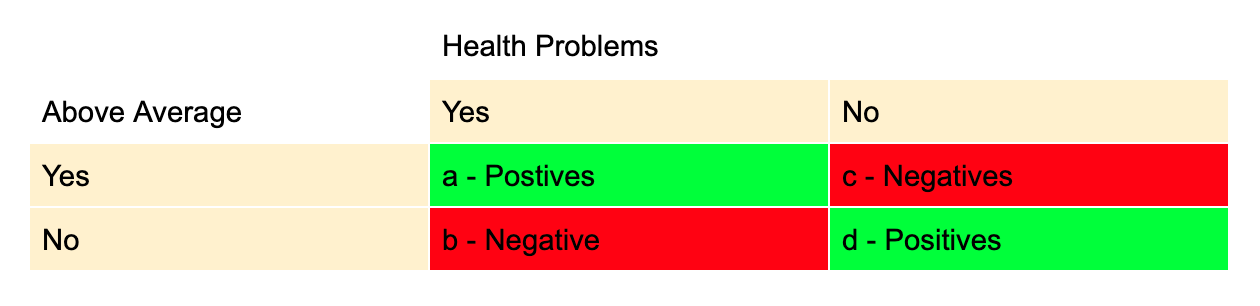



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



2




Image Result For Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



bestpictnjne 人気ダウンロード Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk When To Use Should I Use Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
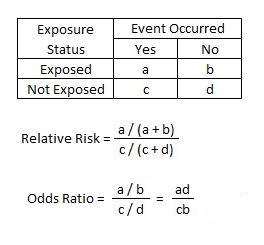



Relative Risk Article




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



2




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
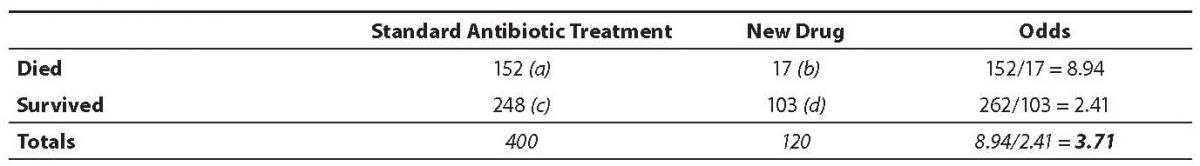



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
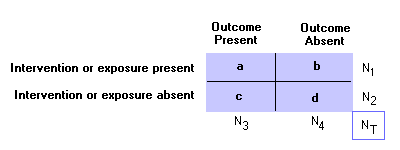



Epidemiology Glossary Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Epidemiology Stepwards




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
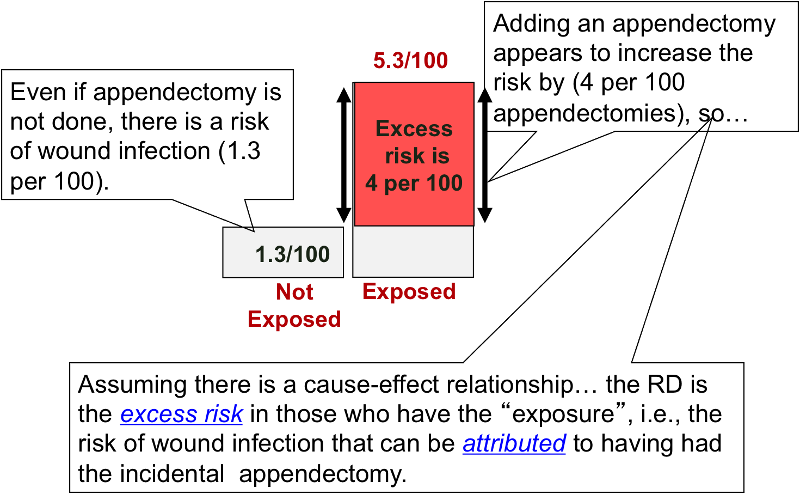



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Sciencedirect




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



1




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Relative Risk Wikipedia



2




Literature Search



1




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿